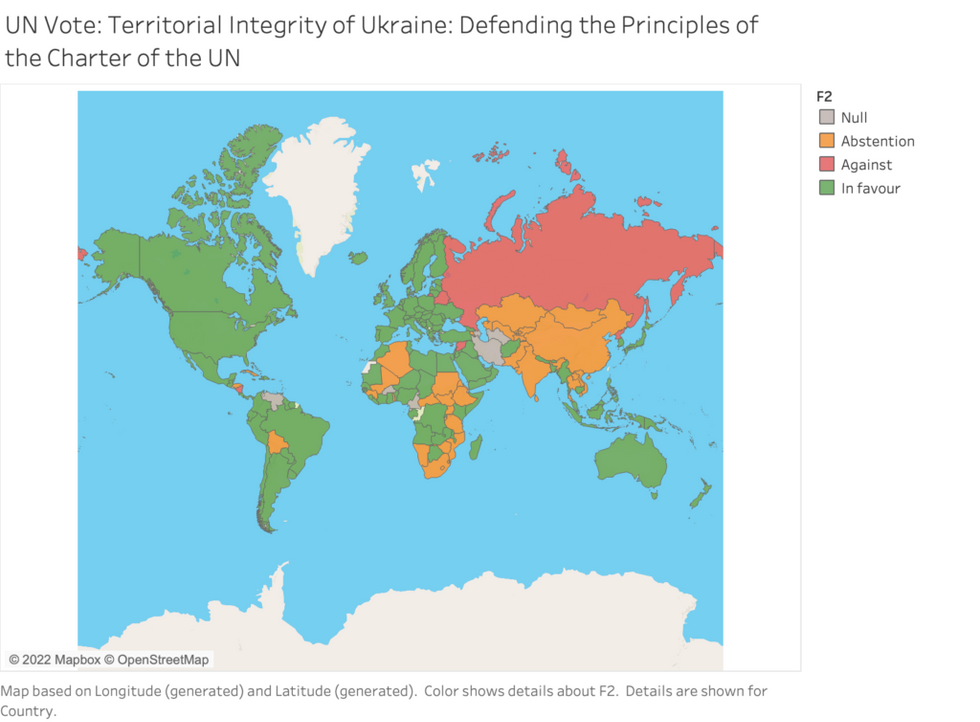
The UN General Assembly voted to condemn Russia’s annexation of four Ukrainian territories on Wednesday. The vote was 143 in favor, five opposed, 35 abstentions and ten absent. Two supporting votes (Myanmar and Afghanistan) were cast by delegates who did not represent their de facto governments. So the actual vote was something on the order of 141 for and the rest checking out or opposing.
Given the egregiously illegal nature of the issue — outright annexation of a neighbor’s sovereign territory — the fact that essentially 52 states did not back its condemnation after what must have been considerable pressure is more than remarkable.
These 52 states were almost entirely from the Global South, with Africa and Asia being the continents whose governments were most inclined to vote against, abstain, or stay home. Southeast Asia was generally not in this camp, though important states such as Vietnam and U.S. treaty ally Thailand abstained.
But Eurasia’s vast expanse, comprising (other than Russia) China, India, Pakistan, Mongolia, and all five Central Asian states that constituted part of the former Soviet Union, and also Iran, were not with the United States on the resolution. Almost all these states also belong to the Shanghai Cooperation Organization — a rising, if still early-stage — international organization representing one of the core geographies of the global order. As many as 24 African states also abstained, opposed, or did not vote for the resolution. With the exception of Cuba, Venezuela, Honduras, El Salvador, Bolivia, and Nicaragua — most of whom Washington has poor or hostile relations with — Latin American and Caribbean governments voted to support the resolution.
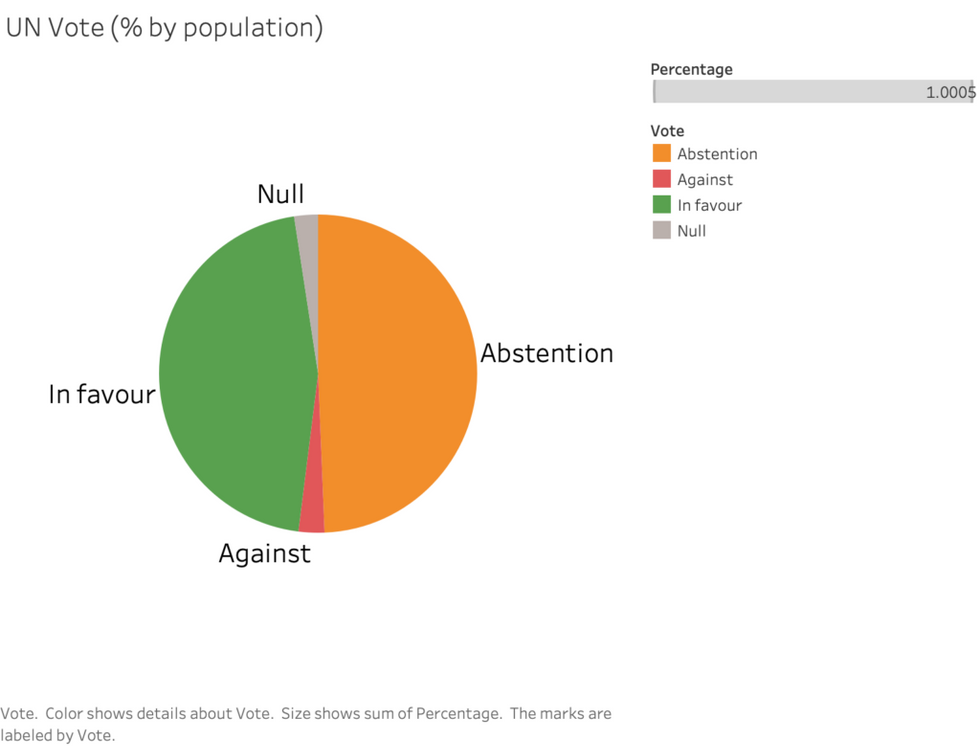
The outcome mirrored almost exactly the General Assembly vote last March to condemn the Russian invasion. Since then, the Russians have been accused of war crimes, while at the same time losing ground on the battlefield in recent weeks. Putin is domestically weaker and a target of nationalist critics. In the last few days, the world watched as Russian rockets pounded civilian targets in several Ukrainian cities. Yet the global dividing lines have barely budged. By population, a majority of the Global South and governments representing nations with close to half of the world’s population did not agree with Washington’s position when put to a public vote.
The fact is that, after nearly eight months of war, a global consensus on the conflict remains elusive. Many key states do not wish to take sides even symbolically since a UNGA resolution by itself cannot be enforced. When it comes to materially backing the U.S. stance with sanctions against Russia, almost no state outside the NATO bloc (minus Turkey) and Japan has enlisted.
President Biden paints the Ukraine war as an existential threat to the global system. His administration’s just-released National Security Strategy said “over the past decade, the Russian government has chosen to pursue an imperialist foreign policy with the goal of overturning key elements of the international order.” Many countries do not like the Russian invasion, but they appear to see the conflict as gray, not black and white, while having important interests to protect. And almost none outside core U.S. allies appear willing to undergo the costs they may bear by punishing Moscow with sanctions. Nearly eight months into this horrific war, and with Russia on the backfoot, this remains the reality.